Functions, Selection, and Iteration
Reading
Key ideas
From chapter 6:
- Be able to write a function.
- Be able to call a function.
- Understand function parameters.
- Understand the difference between a fruitful function and a non-fruitful function.
- Understand the difference between a local variable and a global variable.
From chapter 7:
- The
booltype has valuesTrueandFalse - Boolean operators:
==,!=,>,>=,<,<= - Logical operators:
and,or,not - Conditional statements:
if,ifelse,ifelifelse - Conditional statements can be nested
- Writing and calling Boolean functions
From chapter 8:
- for loop
- Know how to use
range - Know how to iterate over a string (e.g.
"Bozeman High") or a list (e.g.[1, "Potato", 2, "Potato"]) - while loop
- Know how to nest one loop inside of another
Active learning
Activity 1
Modify this file to call the draw_square function multiple times to create this image: 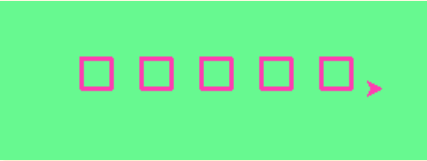
Activity 2
Consider a simplified game of UNO that has forty different cards. Each card has a color (“red”, “yellow”, “green” or “blue”) and a value (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 or 9). One card can be played on top of the the other as long as either the numbers match, the colors match, or both. Complete the boolean function below so that it returns True if the second card can be played on the first card and False otherwise.
def legal_play(first_value, first_color, second_value, second_color):
# your commands here
For example,
legal_play(3, "blue", 3, "green")
and
legal_play(5, "yellow", 7, "yellow")
should both return True, but
legal_play(9, "red", 6, "green")
should return False.
Activity 3
Take key-events.py and modify it so that the turtle only moves if it will still be visible. Use one boolean function in your solution.
Activity 4
Write a Python program that generates a random number between 1 and 10. The program should repeatedly ask the user to guess what the number is until the user guesses correctly. When the user guesses correctly, the program should print a message that shows how many tries it took. For example, the message might be Congratulations! That took 6 guesses.
Activity 5
Write a Python program that asks the user to enter two integers: one for the number of rows and one for the number of columns. The program should then produce a text-based drawing where each position in the drawing is randomly determined with equal probability to be either a “*” or a “-“. For example, with 4 rows and 6 columns, the drawing might look like this:
\*\*-\*-\*
--\*\*--
-\*--\*-
---\*-\*
Activity 6
Python has two keywords that are relevant to loops: continue and break. Determine what they do by experimenting with loop.py. Note: Try to avoid using these two Python constructs. Typically, there is a better way to solve the problem.