Lecture 10: Polymorphism; command line args
Textbook section
2.2
Polymorphism
- literally means “many forms”
- In object oriented design, refers to the ability of a reference variable to take different forms
Command line arguments
- get stored in
String[] args - to run a Java program with command line arguments in Eclipse, go to Run -> Run Configurations… and then edit in the Arguments tab
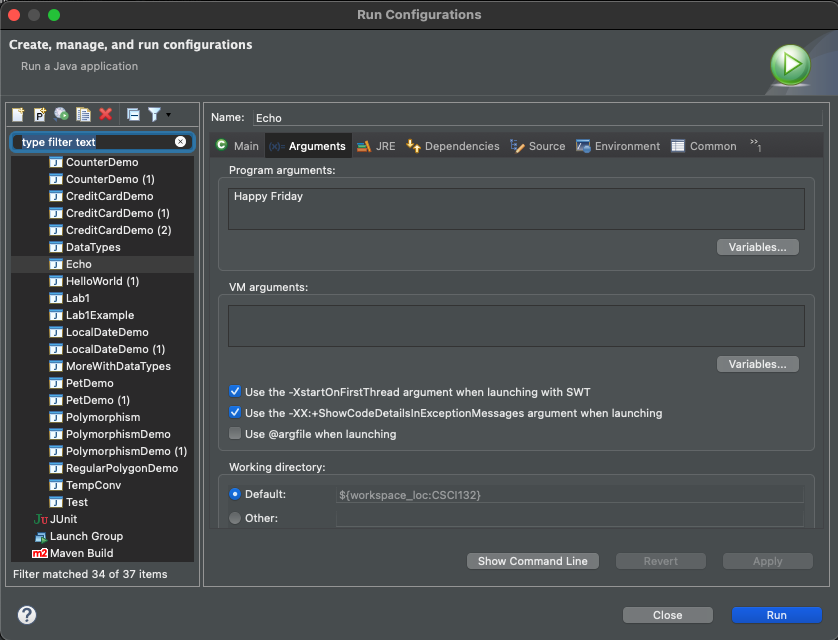
- to run a Java program from terminal, use
javaand then the binary file - you may need to add java to your path (google “add java to path” + your operating system)
Files used in class
Additional exercises
- R-2.11 from book: Consider the following code fragment, taken from some package:
class State extends Region {
State() {}
public void printMe() { System.out.println("Ship it."); }
}
class Region extends Place {
Region() {}
public void printMe() { System.out.println("Box it."); }
}
class Place extends Object {
Place() {}
public void printMe() { System.out.println("Buy it."); }
}
public class Maryland extends State {
Maryland() { /* null constructor */ }
public void printMe() { System.out.println("Read it."); }
public static void main (String[] args) {
Region east = new State();
State md = new Maryland();
Object obj = new Place();
Place usa = new Region();
md.printMe();
east.printMe();
((Place) obj).printMe();
obj = md;
((Maryland) obj).printMe();
usa = md;
((Place) usa).printMe();
}
}
What is the output from calling the main() method of the Maryland class?