Lecture 12: Wrapper classes; exceptions
Textbook sections
1.3; 2.4
Wrapper clases
Because many data structures and algorithms in Java’s libraries are specifically designed to work with objects types, not primitives, Java defines wrapper classes for each primitive type. See this tutorial.
Useful for parsing and changing to strings:
parseInt()method (for example)toString()method
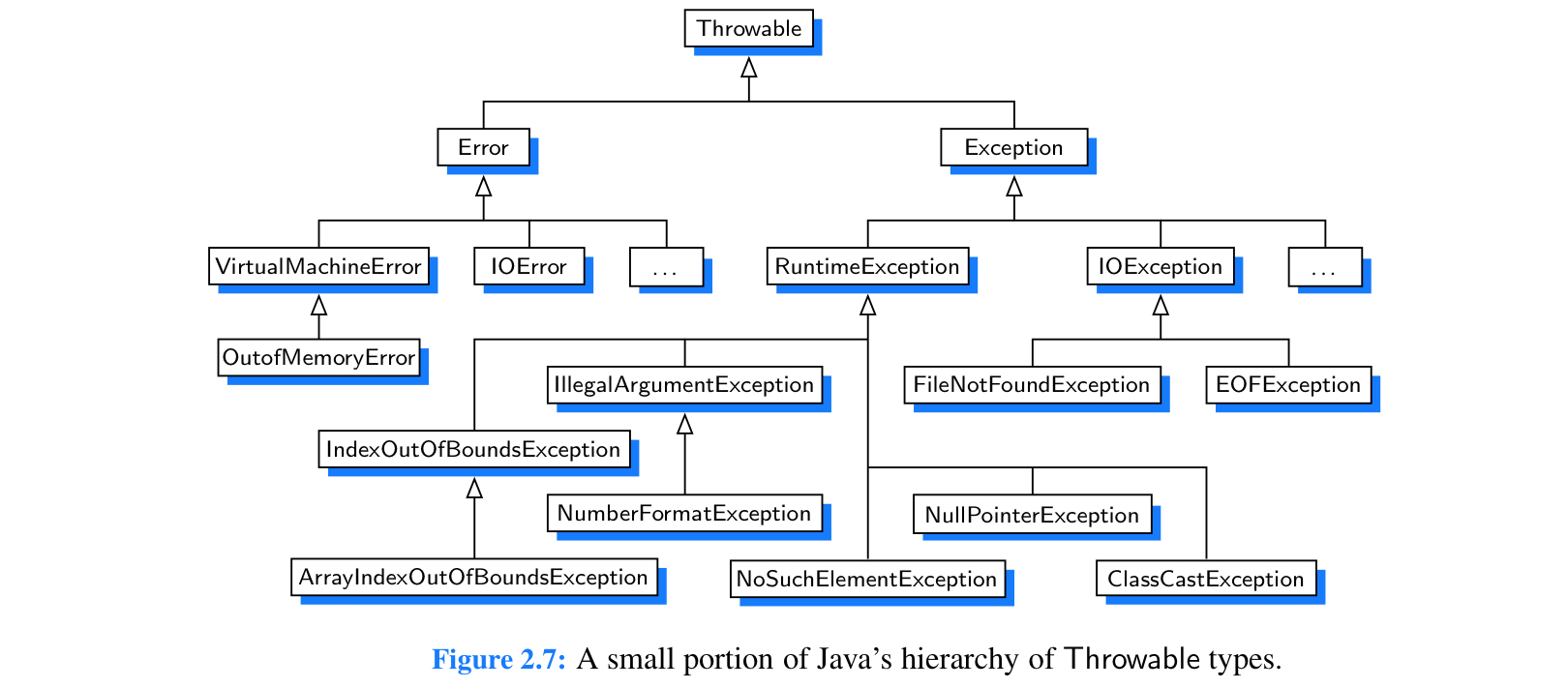
Exceptions
Exceptions are unexpected events that occur during the execution of a program.
We say that an exception is thrown by code that encounters the unexpected situation. We say that the exception is caught by a surrounding block of code that handles the problem in an appropriate fashion.
Catching exceptions in Java
We use try-catch statements to catch exceptions in Java.
try {
// guarded body
} catch (exceptionType1 variable1) {
// remedy body 1
} catch (exceptionType2 variable2) {
// remedy body 2
}
Throwing exceptions in Java
We often instantiate an exception object when we throw it:
throw new exceptionType(parameters);
Files used in class
Additional exercises
Change the ExceptionDemo class to get the input as a command line argument. Add code to catch a ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException and use the DEFAULT value for n.