Lecture 8: Object Oriented Design: Inheritance
Textbook section
2.1-2.2
Object oriented design principles
- Abstraction
- give an interface of an abstract data type (ADT)
- a class implements the interface
- Encapsulation
- do not reveal the implementation details; just maintain the interface
- Modularity
- organize different components of a system into separate functional units
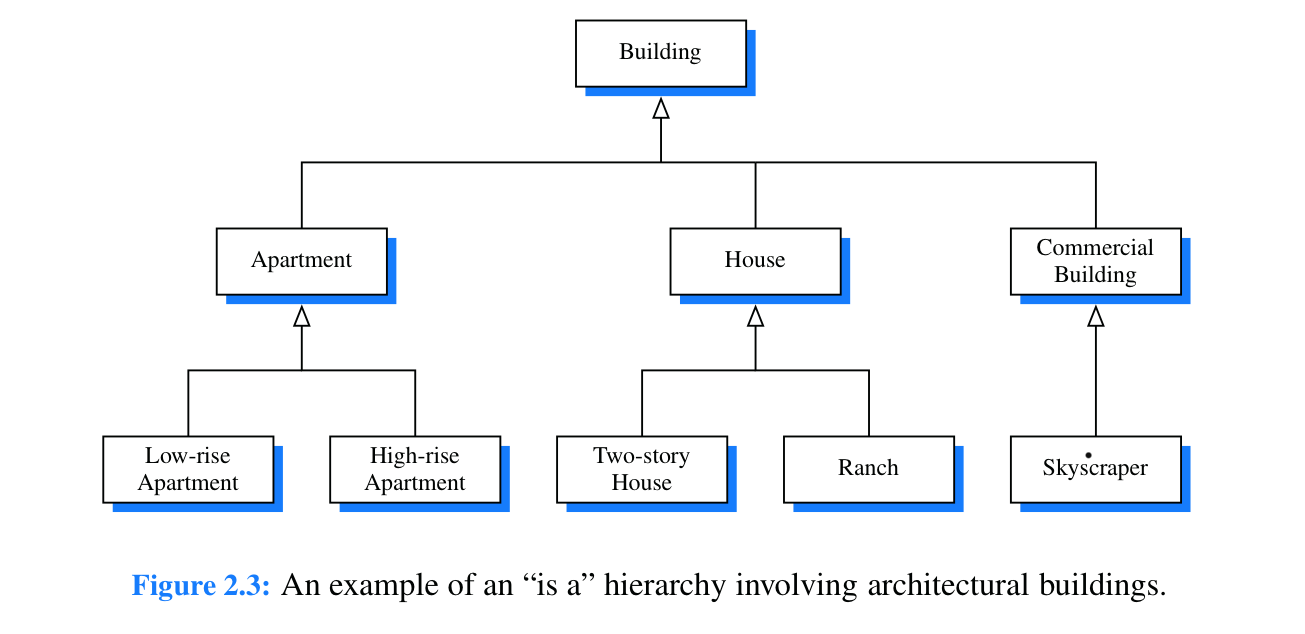
Inheritance
- hierarchical; uses “is-a” relationships
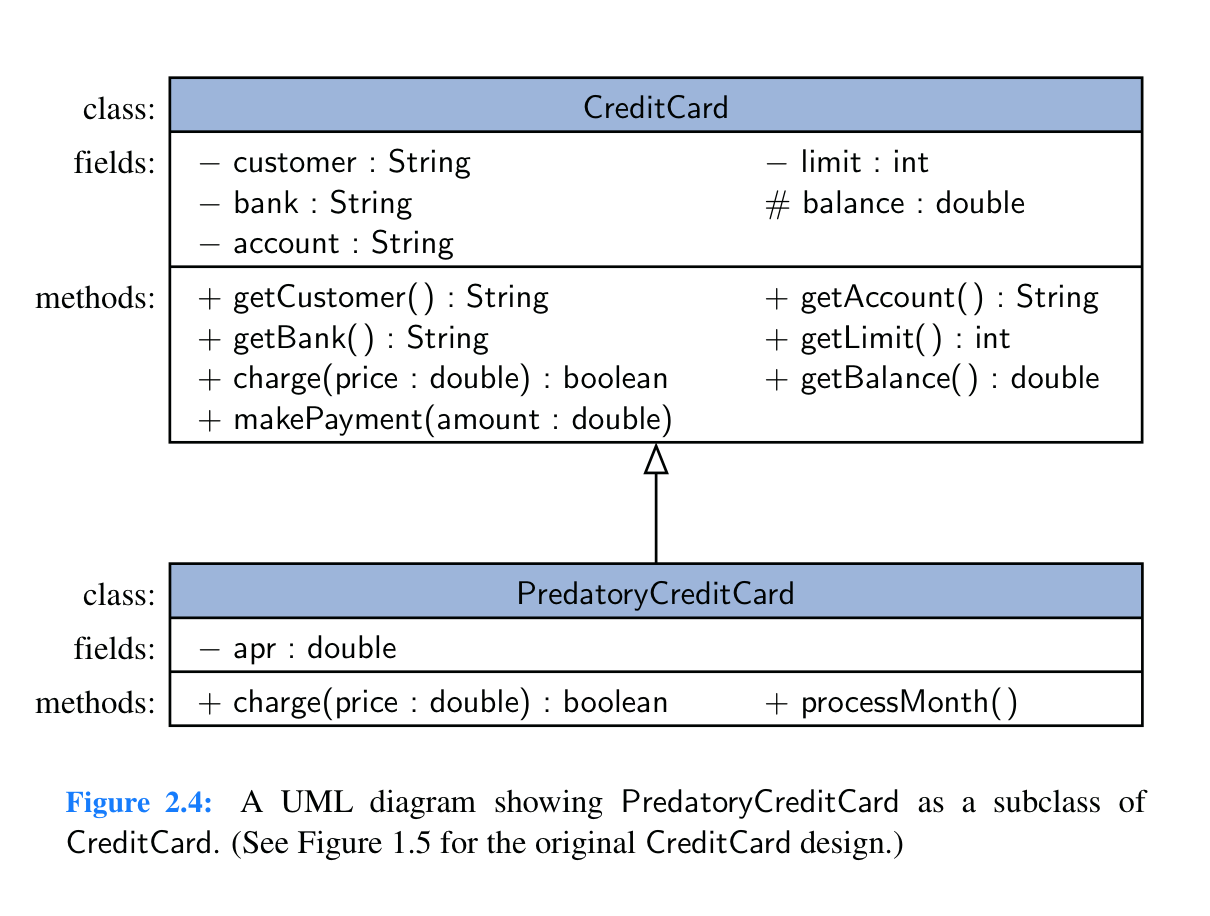
- we say that a subclass or child class extends a base class, parent class, or super class
- child class can augment by adding new fields and methods
- can also override an existing method
- use
superkeyword to refer to parent class - constructors are not inherited
Files used in class
Additional exercises
- Create another class,
AirlineCreditCard, that inherits from theCreditCardclass. It should have the additional private fieldsairline(Stringtype) andmiles(doubletype). It should have a constructor that calls theCreditCardconstructor using thesuperkeyword and sets the values of the two new fields. It should override thechargemethod to also add one mile per dollar spent to themilestotal. (Try to use thesuperkeyword again to call thechargemethod from the parent class.) Add agetMiles()method and write some code inCreditCardDemo.javato test that your new class is working.